The AKT/PKB kinase is activated by PI3K activation or loss of PTEN. Interestingly, about a third of the breast and prostate tumors and majority of the pancreatic tumors that exhibit AKT activation retain normal PTEN and PI3K activity.
Novel AKT Tyr176-phosphorylation, mediated by ACK1 (Pubmed ID: 20333297)
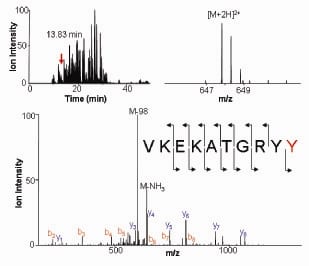
We have uncovered a novel signaling mechanism wherein ACK1 directly phosphorylated AKT at Tyr176 (Figure 1). For membrane localization, AKT anchors to Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate or PIP3. However, Tyr176-phosphorylated AKT bound another membrane phospholipid, phosphatidic acid (PA). Further, Tyr176-phosphorylated AKT translocated to the membrane leading to its Ser473-phosphorylation and kinase activation. Pubmed ID: 20333297
AKT Tyr176-phosphorylation in Prostate and breast cancers
We generated ACK1 transgenic mice that not only exhibited AKT Tyr176-phosphorylation but also developed prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PINs) and rare carcinomas. Pubmed ID: 20333297
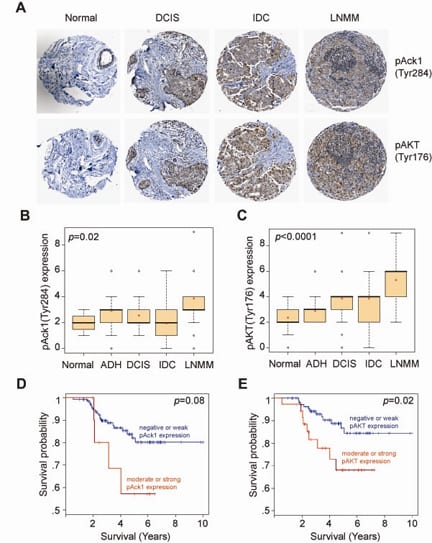
The most significant role of pY176-AKT was observed in progression of breast cancer (Figure 2A). The expression levels of pY176-AKT and activated ACK1 were positively correlated with the severity of breast cancer progression (Figure 2B and C), and inversely correlated with the survival of patients (Figure 2D and E). Pubmed ID: 20333297