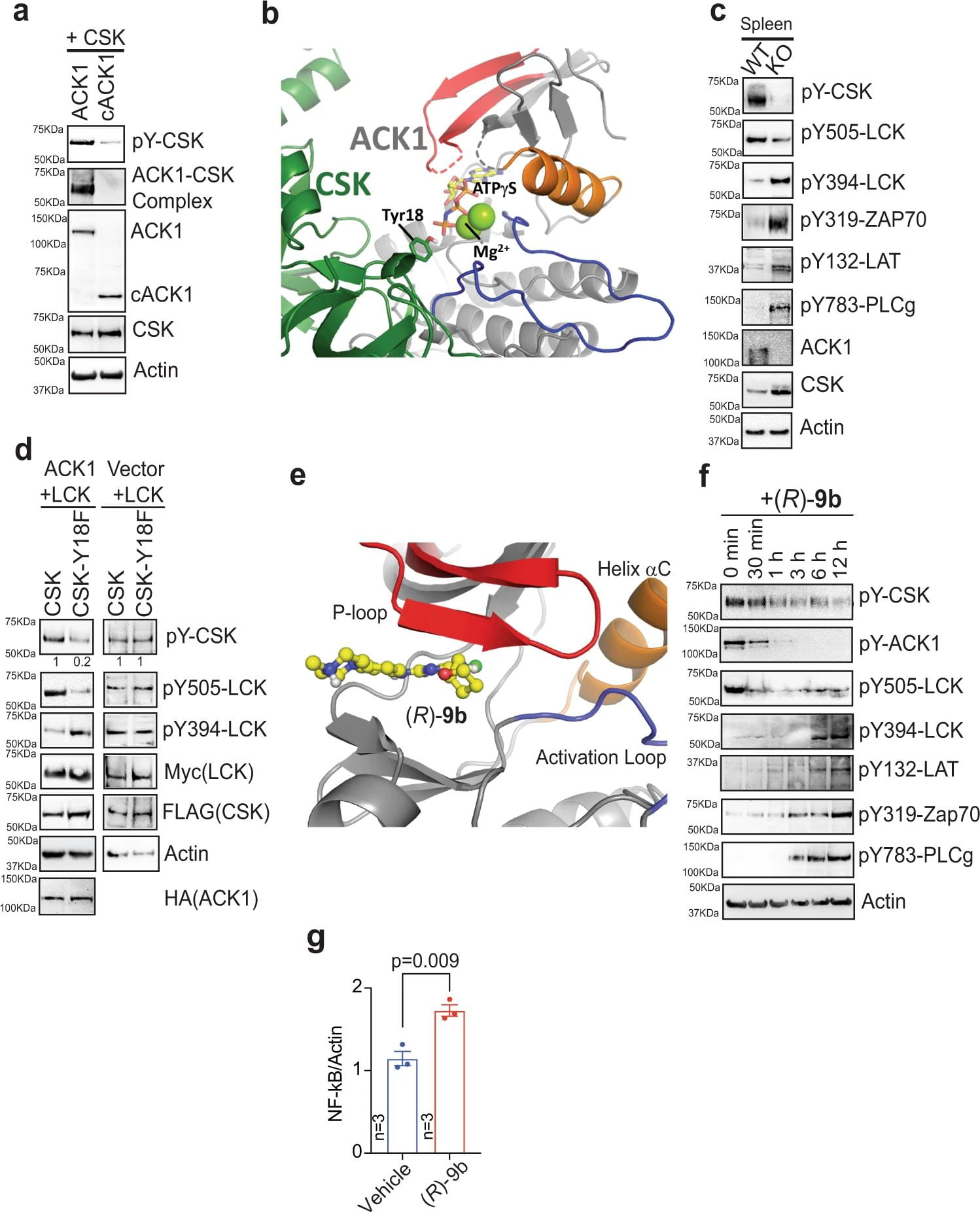
Solid tumors are highly refractory to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapies due to the functional impairment of effector T cells and their inefficient trafficking to tumors. T-cell activation is negatively regulated by C-terminal Src kinase (CSK); however, the exact mechanism remains unknown. We uncovered that ACK1 phosphorylate CSK at Tyrosine 18 (pY18), which enhances CSK function, constraining T-cell activation. Mice deficient in the ACK1/Tnk2 exhibit spontaneous activation of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, resulting in inhibited growth of transplanted ICB-resistant tumors. Furthermore, ICB treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patients results in re-activation of ACK1/pY18-CSK signaling, confirming the involvement of this pathway in ICB insensitivity. An ACK1 small-molecule inhibitor, (R)-9b, recapitulates inhibition of ICB-resistant tumors, which provides evidence for ACK1 playing a pivotal role in generating ICB resistance (Figure 1). Nature Communications, 2022.
ACK1-AR SIGNALING IN PROSTATE CANCER
ACK1 (TNK2) interacts with androgen receptor or AR in an androgen-independent manner. Expression of activated ACK1 correlates positively with the progression of disease to CRPC stage, and PC patients whose tumors display moderate to strong staining of activated ACK1 have poor prognosis.
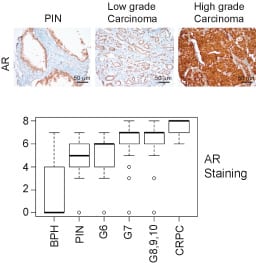
AR plays a paramount role in the onset and progression of prostate cancer (PC). A majority of the PC patients progress to a lethal stage of the disease, referred to as the metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC). There is increasing expression of AR as disease progress to later stages (Figure 2). CRPC remains an incurable malignancy with limited treatment options.
Need to venture beyond Anti-Androgen Therapies
Reliance of CRPCs on AR despite androgen-depletion, has led to development of AR antagonists, Enzalutamide & Abiraterone. Unfortunately, in spite of early response, most patients relapsed within 2 years, exhibiting renewed AR activity.
ACK1, a new target in CRPCs
ACK1 is upregulated in ~40% of prostate adenocarcinomas. Importantly, 10 out of 13 CRPCs exhibited ACK1 overexpression. Further, LNCaP cells that are poorly tumorigenic in castrated mice, formed robust CRPC tumors following expression of activated ACK1.
ACK1, a histone kinase
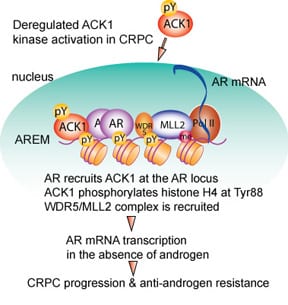
We uncovered that ACK1 interacts with AR and deposit novel epigenetic marks, histone H4 Tyr88-phosphorylation (Figure 3). Inhibition of ACK1 by (R)-9b suppressed AR & AR-V7 transcription, inhibiting proliferation of enzalutamide-resistant CRPC tumors.
- Mahajan K, Malla P, Kim J, Coppola D, Lawrence N and Mahajan NP*. ACK1 regulates histone Tyr-phosphorylation and AR gene expression in castration resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2017. Pubmed ID: 28609657