Three mechanisms of ACK1 activation
(i) ACK1 integrates signals from various receptor tyrosine kinases, e.g. MERTK, EGFR, PDGFR, Insulin receptor, HER2. These kinases activate ACK1 in multiples cancers, including prostate, breast, lung, gastric and many other cancers.
(ii) ACK1/TNK2 gene is amplified in 40% of lung cancers, 30% of breast cancers and 10% of prostate cancers.
(iii) Autoactivating mutations
Identification of ACK1 inhibitor, (R)-9b
In spite of its significance, no ACK1 inhibitor has so far made it to clinical trial. We generated a new class of small molecule ACK1 inhibitor (R)-9b (Figure 1), that has excellent drug-like properties. (R)-9b suppressed proliferation of various prostate, breast and lung xenograft tumor growth.
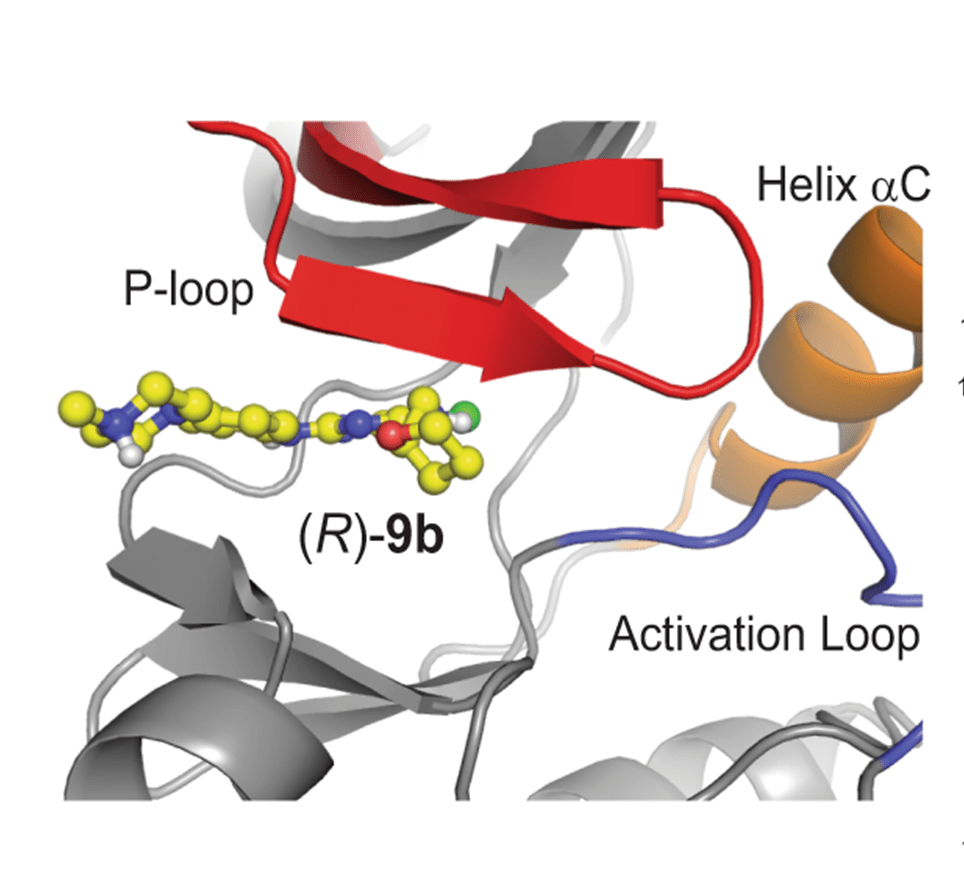
Crystal structure of (R)-9b bound to ACK1
Recently with our collaborators, we have solved the crystal structure of (R)-9b bound to ACK1 kinase domain (Figure 2) Nature Communications, 2022.
Pre-IND GLP-Tox studies with (R)-9b
(R)-9b has excellent ADME properties and exhibited no toxicity in rats and dogs even at high dosage. It also has oral efficacy.
Clinical Trial of ACK1 inhibitor, (R)-9b
Clinical trial of (R)-9b is expected to start in 2023. Dr. Nupam Mahajan nupam@wustl.edu can be contacted by interested parties.